Pimples, those tiny but annoying skin eruptions, have plagued almost everyone at some point in their lives. These small bumps, often characterized by redness and discomfort, can seemingly appear out of nowhere and become a source of frustration and self-consciousness. However, there’s more to pimples than meets the eye. In this comprehensive article, we will delve into the science behind pimples, understanding what causes them to form and exploring effective strategies to beat them and achieve clear, blemish-free skin.
Understanding Pimples: What Are They?
Before we embark on our journey to conquer pimples, it’s essential to have a clear understanding of what they are and how they develop.
What Are Pimples?
Pimples, also known as acne vulgaris, are a common skin condition characterized by the formation of small, raised bumps on the skin’s surface. These blemishes typically appear on the face, neck, chest, back, and shoulders, areas where the skin has a high concentration of oil glands.
How Do Pimples Develop?
To comprehend the science behind pimples, it’s vital to understand their development process. Pimples begin to form when hair follicles, the tiny sacs in the skin that house hair and sebaceous (oil) glands, become clogged. This blockage is usually caused by a combination of factors, including excess oil production, dead skin cells, and bacterial growth.
The formation of a pimple can be broken down into the following steps:
- Excess Oil Production: Our skin’s sebaceous glands produce oil, known as sebum, to keep it moisturized and protected. However, when these glands produce too much oil, it can mix with dead skin cells and become trapped in the hair follicles.
- Clogged Pores: As the excess oil and dead skin cells accumulate, they form a plug within the hair follicle, obstructing its normal function. This plug is known as a comedone.
- Bacterial Growth: The bacterium Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), which naturally resides on the skin, thrives in this oily, anaerobic (oxygen-deprived) environment. P. acnes can multiply within the clogged follicle, leading to inflammation and infection.
- Inflammation: As the bacteria multiply, the body’s immune response is triggered, resulting in inflammation. This inflammation is what causes the redness, swelling, and discomfort associated with pimples.
Types of Pimples:
Pimples can take various forms, each with its own characteristics:
- Blackheads (Open Comedones): Non-inflammatory, these are open pores with a darkened plug at the surface. The dark color is due to oxidation, not dirt.
- Whiteheads (Closed Comedones): Non-inflammatory, these are closed pores with a small white bump just below the skin’s surface.
- Papules: Small, red, and tender bumps that result from inflammation and infection of the hair follicles.
- Pustules: Similar to papules but filled with pus. These are often referred to as “pimples.”
- Nodules: Large, painful, solid lumps that develop beneath the skin’s surface due to severe inflammation.
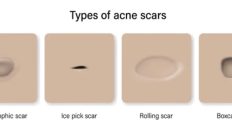
- Cysts: The most severe form of pimple, cysts are painful, pus-filled lumps that can lead to scarring if not treated promptly.
Now that we understand the basics of pimple formation, let’s explore the science behind what causes them and how to effectively combat them.
The Science Behind Pimples: Causes and Contributors
Pimple formation is influenced by several factors, and understanding these causes is vital for developing effective strategies to beat them:
1. Hormonal Fluctuations:
Hormones, especially androgens (male hormones), play a substantial role in the development of pimples. Androgens stimulate the sebaceous glands to produce more oil, increasing the likelihood of clogged pores and acne breakouts. This is why acne is often most prevalent during puberty, when hormone levels surge.
2. Genetics:
Genetics can also contribute to an individual’s susceptibility to pimples. If your parents or siblings had acne, you may be more prone to developing it as well. Genetic factors can influence the skin’s oil production, inflammation response, and overall predisposition to acne.
3. Excess Oil Production:
Overactive sebaceous glands produce more oil than necessary, leading to the accumulation of excess sebum within the hair follicles. This excess oil can block pores and contribute to pimple formation.
4. Dead Skin Cells:
The outer layer of our skin continuously sheds dead skin cells as part of its natural renewal process. However, sometimes these cells do not slough off effectively and can accumulate, especially when combined with excess oil. This accumulation can clog pores and serve as a breeding ground for bacteria.
5. Bacterial Growth:
Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) is a bacterium that naturally resides on our skin. It plays a role in the development of pimples when it multiplies within clogged pores, leading to inflammation and infection. P. acnes thrives in the oxygen-deprived environment created by the blocked follicles.
6. Inflammation:
Inflammation is a crucial aspect of the pimple development process. When P. acnes proliferates within the clogged hair follicle, the body’s immune response is triggered, resulting in redness, swelling, and discomfort.
7. Diet:
While the link between diet and pimples is complex and varies from person to person, some individuals find that certain dietary factors, such as high-glycemic-index foods and dairy products, can exacerbate acne.
8. External Factors:
Environmental factors, including exposure to pollution, humidity, and friction from tight clothing or headgear, can contribute to pimple formation or aggravation.
Beating Pimples: Effective Strategies for Clearer Skin
Now that we’ve delved into the science behind pimples and their causes, let’s explore a range of effective strategies to help you beat them and achieve clearer, healthier skin.
1. Establish a Consistent Skincare Routine:
A daily skincare routine forms the foundation of pimple management. Here are the key steps to include:
- Cleansing: Use a gentle, non-comedogenic cleanser to remove excess oil, dirt, and impurities from your skin.
- Exfoliating: Incorporate a mild exfoliant with ingredients like salicylic acid or glycolic acid 2-3 times a week to help unclog pores and remove dead skin cells.
- Moisturizing: Even if you have oily skin, use a lightweight, non-comedogenic moisturizer to maintain skin hydration.
- Sun Protection: Always apply sunscreen with an SPF of at least 30 to protect your skin from UV damage. Some acne treatments can make the skin more sensitive to the sun.
2. Choose the Right Products:
Select skincare products that match your skin type and concerns. Look for labels like “oil-free,” “non-comedogenic,” and “hypoallergenic.” Avoid harsh, abrasive products that can irritate the skin and exacerbate pimples.
3. Topical Treatments:
Over-the-counter and prescription topical treatments can be valuable in managing pimples. These treatments may contain ingredients such as:
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Kills acne-causing bacteria and helps unclog pores.
- Salicylic Acid: Exfoliates the skin’s surface and helps prevent pore blockage.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids promote skin cell turnover and prevent clogged pores.
Consistency in applying these products and adherence to your dermatologist’s prescription recommendations are essential.
4. Hormonal Treatments:
For individuals with hormonal acne, hormonal treatments may be beneficial. Birth control pills and medications like spironolactone can help regulate hormone levels and reduce acne flare-ups.
5. Lifestyle Modifications:
Certain lifestyle changes can significantly impact pimple management:
- Diet: Although the relationship between diet and pimples is individualized, some people find that reducing their intake of high-glycemic-index foods and dairy products can help improve their skin.
- Stress Management: Elevated stress levels can exacerbate pimples. Consider incorporating stress-reduction techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises into your daily routine.
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity promotes circulation and can help reduce stress. After exercising, be sure to shower and cleanse your skin to prevent sweat-induced pimples.
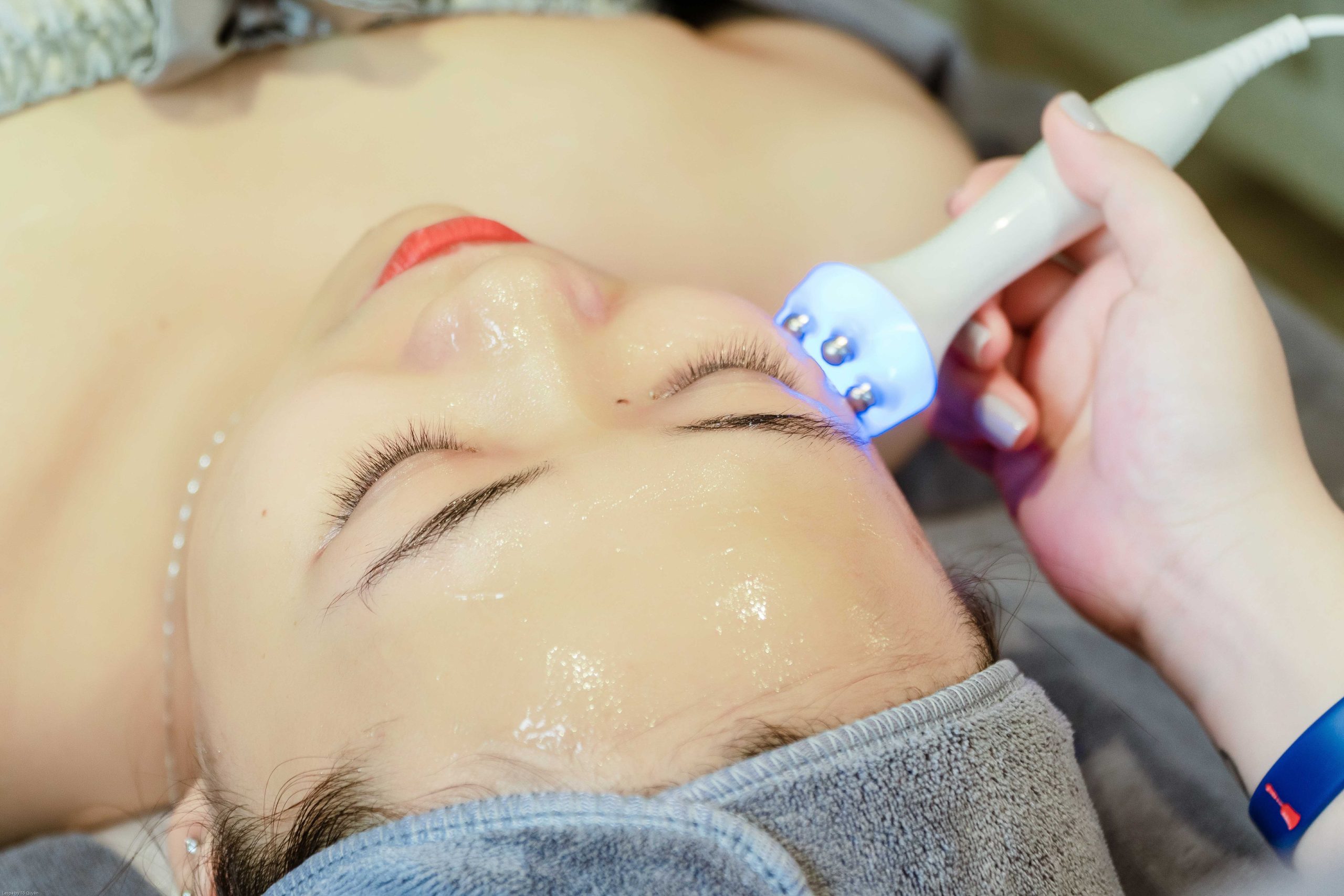
6. Professional Treatments:
Dermatologists offer a range of professional treatments to help conquer pimples:
- Chemical Peels: These treatments use exfoliating acids to remove the top layer of skin, helping unclog pores and improve skin texture.
- Microdermabrasion: A non-invasive procedure that uses a machine to exfoliate the skin’s surface, reducing the visibility of acne scars.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can target acne-causing bacteria and reduce inflammation, resulting in clearer skin.
7. Avoid Picking and Squeezing:
Resist the urge to pop or pick at pimples. These actions can lead to infection, scarring, and further inflammation. Instead, rely on proper skincare and treatment products to address blemishes.
8. Seek Professional Guidance:
For individuals dealing with severe, persistent, or scarring pimples, it’s essential to consult a dermatologist. Dermatologists can develop personalized treatment plans tailored to your unique skin type and acne severity, which may include prescription medications.
Conclusion
Pimples, though often frustrating and bothersome, are a common skin condition with roots in science and biology. By understanding the factors that contribute to pimple formation and employing effective strategies to manage and prevent them, you can achieve clearer, healthier skin and boost your self-confidence. Remember that everyone’s skin is unique, and it may take some trial and error to find the most effective approach for you. With patience, dedication, and a well-informed skincare routine, you can beat pimples and reclaim your confidence, allowing your natural radiance to shine through.