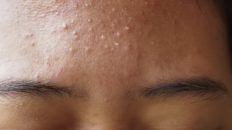
Types of Acne Scars
- Atrophic Scars:
- Icepick Scars: Narrow, deep pits that resemble small puncture marks.
- Boxcar Scars: Wider, rectangular depressions with defined edges.
- Rolling Scars: Broad, shallow depressions with a wavy or rolling appearance.
- Hypertrophic Scars:
- Raised, thickened scars that result from excess collagen production during the healing process.
- More common on the chest, back, and shoulders.
Factors Contributing to Scar Formation
Acne scars develop due to various factors:
- Inflammation: Severe inflammation damages collagen, leading to atrophic scars.
- Delayed or Inadequate Treatment: Untreated or improperly managed acne is more likely to result in scarring.
- Genetics: A person’s genetic predisposition can influence scar formation.
- Skin Type: Individuals with darker skin tones may be more prone to hyperpigmentation and keloid scars.
- Picking or Squeezing Pimples: This can introduce more bacteria and worsen inflammation, increasing the likelihood of scars.
Prevention of Acne Scarring
Early and Effective Acne Treatment
The best way to prevent acne scarring is to manage acne effectively from the start:
- Consult a dermatologist for personalized treatment plans.
- Follow prescribed medications and skincare routines.
- Avoid picking, squeezing, or scratching pimples to reduce the risk of further damage.
Sun Protection
Protecting your skin from the sun is crucial to minimize the appearance of scars:
- Use broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily.
- Wear protective clothing and wide-brimmed hats.
- Avoid prolonged sun exposure, especially during peak hours.
Professional Treatments for Acne Scarring
Dermatological Options
Dermatologists offer several treatments to improve the appearance of acne scars:
- Chemical Peels: Chemical solutions are applied to the skin to remove the top layer, revealing smoother skin underneath.
- Microdermabrasion: A machine exfoliates the skin’s surface, reducing the visibility of scars.
- Microneedling: Tiny needles create controlled micro-injuries, stimulating collagen production and improving texture.
- Laser Therapy: Various laser and light-based treatments target scar tissue, promoting skin remodeling.
- Fillers for Volume Correction: Dermal fillers can temporarily raise depressed scars to the level of the surrounding skin.
The Importance of Consulting a Dermatologist
While some over-the-counter treatments and home remedies can help, consulting a dermatologist is crucial for effective scar management. Dermatologists can assess your specific scar types and recommend the most suitable treatments, often resulting in more significant improvements.
Topical Treatments for Acne Scarring
Topical Retinoids
Prescription retinoids like tretinoin can help reduce the appearance of acne scars by promoting collagen production and skin renewal.
Silicone Gels and Sheets
These products can be applied directly to scars and help hydrate the skin while flattening and softening scar tissue.
Vitamin C Serums
Vitamin C can aid in skin rejuvenation and improve the overall appearance of scars, especially when used consistently.
Home Remedies and Over-the-Counter Options
Natural Remedies
Some individuals find relief from the appearance of scars by using natural remedies like aloe vera gel, honey, or rosehip oil. While these options may offer mild improvements, they are not as effective as professional treatments.
Over-the-Counter Scar Creams and Gels
Various scar creams and gels are available over the counter, containing ingredients like onion extract, which may help improve the appearance of scars.
Combining Treatment Methods
For the best results, consider combining treatment methods:
- Consult with a dermatologist to create a comprehensive scar management plan.
- Use topical treatments as directed while undergoing professional treatments.
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine to support scar healing.
Lifestyle and Skincare for Scar Management
Sun Protection and SPF Usage
Consistent sun protection is crucial to prevent hyperpigmentation and protect the healing skin.
Proper Hydration and Moisturization
Well-hydrated skin is more resilient and can better heal and repair itself.
Gentle Exfoliation and Skin Renewal
Exfoliating the skin regularly can help remove dead skin cells, allowing new skin to emerge.
Diet and Nutrition
A balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants can support overall skin health.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Coping with Emotional Impact
Dealing with the emotional impact of acne scarring can be challenging:
- Seek support from friends, family, or support groups.
- Consider counseling or therapy to address self-esteem and body image issues.
Building Self-Esteem and Self-Acceptance
Remember that your worth is not defined by your skin’s appearance:
- Focus on your positive qualities and accomplishments.
- Practice self-acceptance and self-compassion.
Surgical Options for Severe Scarring
In severe cases, surgical interventions may be necessary:
- Punch Excisions: Individual scars are removed and closed with sutures.
- Subcision: A procedure to release tethered scars from the underlying tissue.
- Dermal Fillers: Injectable fillers can raise depressed scars.
Conclusion
In conclusion, managing acne scarring requires a multifaceted approach, combining professional treatments, topical options, lifestyle choices, and emotional support. While complete scar removal may not always be possible, significant improvements can be achieved with patience, consistency, and the guidance of dermatological experts. Remember that your self-worth extends far beyond the appearance of your skin, and with the right care, you can regain confidence and embrace your natural beauty.